SECTION 1: Understanding APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
Definition of API
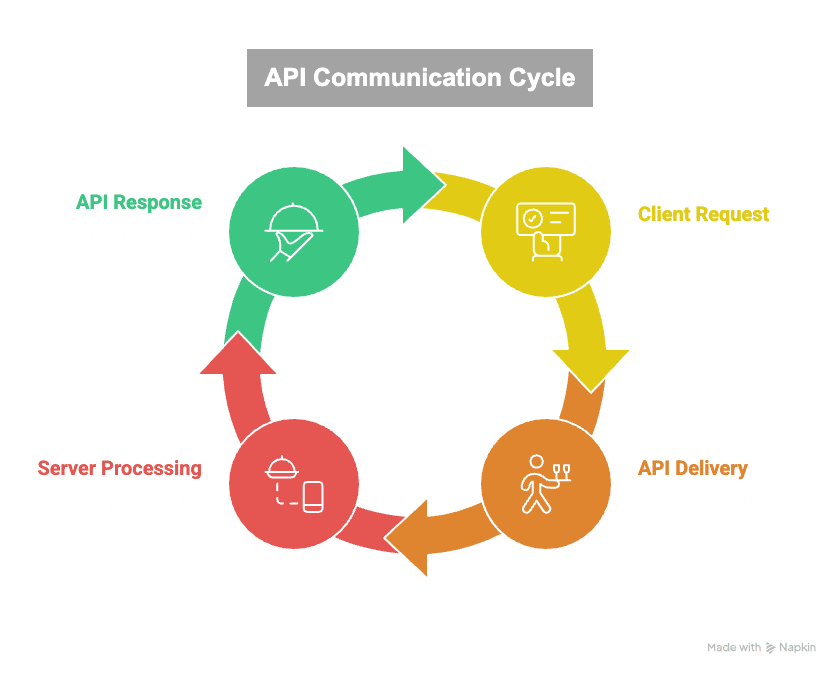
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a software intermediary that allows two applications to communicate with each other.
How APIs Work:
- Requesting Data:
- Your app (like Gmail) sends a request to a server.
- Server Processes Request:
- The server (e.g., Gmail’s servers) receives the request.
- Returning Data:
- The server sends back the required data, typically formatted in JSON (JavaScript Object Notation).
Analogy:
- Think of an API as a waiter in a restaurant.
- You (client) place an order.
- The waiter (API) delivers it to the kitchen (server).
- The waiter then returns with your meal (response).
Two Types of API Requests:
- GET Request – Retrieves data from a server (e.g., read your Gmail inbox).
- POST Request – Sends data to a server (e.g., send an email).
Pre-Made Integrations:
- Google Sheets
- Gmail
Custom Tools:
- If pre-made integrations don’t meet your needs, you can create custom tools using APIs and backend functions.
SECTION 2: Core Components of an AI Agent
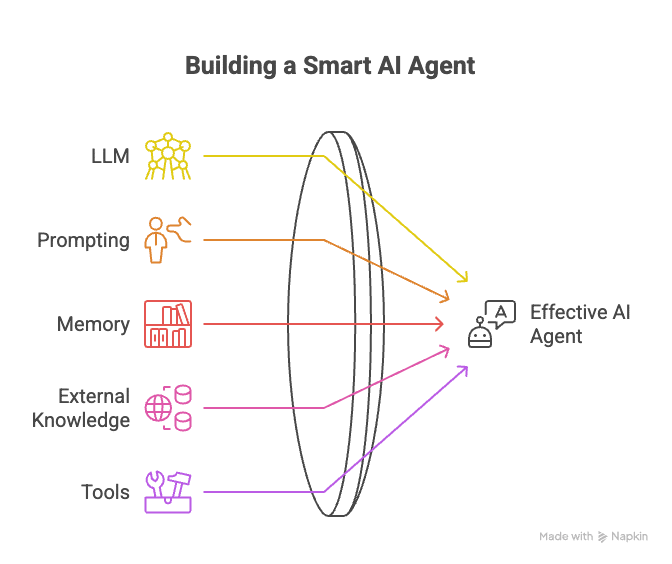
To build a smart, functioning AI agent, you’ll need these five essential components:
- LLM (Large Language Model):
- The AI’s “brain” that understands and generates human-like responses.
- Prompting (Instructions):
- Clear, structured inputs to guide the AI in generating useful outputs.
- Memory:
- Allows the AI to recall past interactions or important information.
- External Knowledge:
- Connects the AI to databases or APIs for up-to-date facts.
- Tools:
- Software or services (e.g., APIs, search engines) the AI uses to perform tasks.
Simplified View: The 3 Key Ingredients to Start
- External Knowledge (like APIs or databases)
- Tools (code libraries, services)
- Prompting (how you instruct the AI)
SECTION 3: From Function to API
A function (e.g., written in Python) performs a specific task.
- When wrapped with an API, it becomes accessible from the web.
- This enables you to send data to the function and get results back.
Example Flow:
- Input: text (e.g., “hello”)
- Function: transforms it (e.g., changes to uppercase)
- Output: TEXT (“HELLO”)
Now, this function can be part of a tool your AI agent uses to perform tasks.
SECTION 4: AI Agent + API Functionality
- Your AI agent sends input to the function via an API.
- The function processes the input and returns an output.
- The agent understands how to use it based on clear documentation.
AI Agent Comprehension Essentials:
- What the tool does
- What information it needs as input
- What information to expect as output
Clear API documentation helps AI agents understand how to use tools correctly.